
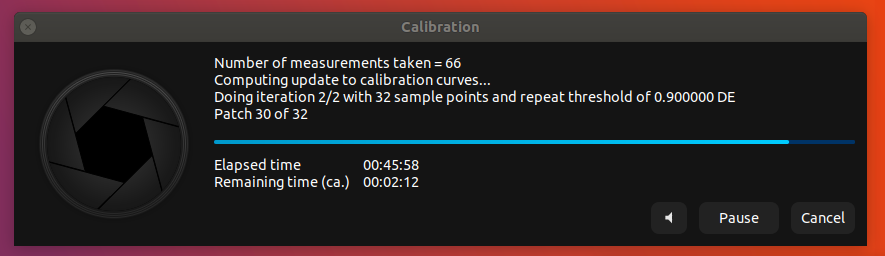
- #Displaycal scanner Patch
- #Displaycal scanner software
- #Displaycal scanner windows 7
- #Displaycal scanner windows
Linux and older versions of Windows require using a standalone LUT loader.
#Displaycal scanner windows 7
Windows 7 onward allows loading calibration curves, though this functionality must be enabled manually. macOS has built-in support for loading calibration curves and installing a system-wide color profile. If a monitor was calibrated before it was profiled, the profile will only yield correct colors when used on the monitor with the same calibration (the same monitor control adjustments and the same calibration curves loaded into the video card's lookup table). Calibration alone does not yield accurate colors. Seeing correct colors requires using a monitor profile-aware application, together with the same calibration used when profiling the monitor. icc files - the difference is only in the name. For convenience, the calibration settings are usually stored together with the profile in the ICC file. The second step, profiling (characterization), involves measuring the calibrated display's response and recording it in a color profile. The calibration settings are stored in a. The first step, calibration, is done by adjusting the monitor controls and the output of the graphics card (via calibration curves) to match user-definable characteristics, such as brightness, white point and gamma.
#Displaycal scanner Patch
#Displaycal scanner software
for input devices (scanner, camera, etc.) a color target which the profiling software will compare to the manufacturer-provided color values of the target.Color-managed applications that are configured to use a correct monitor profile and input/output profiles, with support for control over the rendering intent and black point compensation.Correctly loaded video card LUTs (or monitor profiles that do not require LUT adjustments).Accurate device profiles obtained with source or output characterization software.Requirements for a color-managed workflow The popular Ubuntu Linux distribution added initial color management in the 11.10 release (the "Oneiric Ocelot" release). Additionally, certain hardware, such as most printers and certain monitors, can be calibrated under another OS and then used in a fully color-managed workflow on Linux. This can be used as a workaround for the lack of support for certain spectrophotometers or colorimeters under Linux: one can simply produce a profile on a different OS and then use it in a Linux workflow. Hence, a profile produced on one OS should work on any other OS given the availability of the necessary software to read it and perform the gamut conversions. Since ICC color profiles are written to an open specification, they are compatible across operating systems. Some hardware devices for color calibration lack Linux drivers, firmware or accessory data.The absence of a central user control panel for color settings.
Although it is now possible to obtain a consistent color-managed workflow under Linux, certain problems still remain: This situation is now being progressively remedied, and color management under Linux, while functional, has not yet acquired mature status. Historically, color management was not an initial design consideration of the X Window System on which much of Linux graphics support rests, and thus color-managed workflows have been somewhat more challenging to implement on Linux than on other OS's such as Microsoft Windows or macOS. Gamut conversions, based on accurate device profiles, are the essence of color management. These applications perform gamut conversions between device profiles and color spaces. Linux color management relies on the use of accurate ICC ( International Color Consortium) and DCP (DNG Color Profile) profiles describing the behavior of input and output devices, and color-managed applications that are aware of these profiles. In particular, color management attempts to enable color consistency across media and throughout a color-managed workflow. Linux color management has the same goal as the color management systems (CMS) for other operating systems, which is to achieve the best possible color reproduction throughout an imaging workflow from its source (camera, video, scanner, etc.), through imaging software ( Digikam, darktable, RawTherapee, GIMP, Krita, Scribus, etc.), and finally onto an output medium ( monitor, video projector, printer, etc.). Color profile viewer on KDE Plasma 5, showing an ICC color profile


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
